Steering Ratio – Suspension KPI
Steering ratio is a ratio of the degrees of steering wheel angle input and degrees of road wheel toe angle change.
Steering ratio is a function of rack ratio (mm of rack travel per steering wheel revolution) and suspension geometry. The primary suspension geometry measure is steering lever arm length. Steering arm length is the shortest distance between the suspension steer axis and the steering rack attachment to the wheel carrier.
Broadly speaking steering ratios below ~13-14 are considered fast with ratios above ~18 are slow. The steering ratios of some production sports cars are listed below:
- 2016 MX-5: 15.5
- 2014 911 turbo: 12.3 to 15.0 (variable)
- 2007 Lancer Evo 10: 13.8
- 2004 E46 M3 CSL: 14.5
- 2000 E46 M3: 15.4
- 1999 Honda s2000: 13.8
- 1989 E30 M3: 20.5 (Non-power assisted)
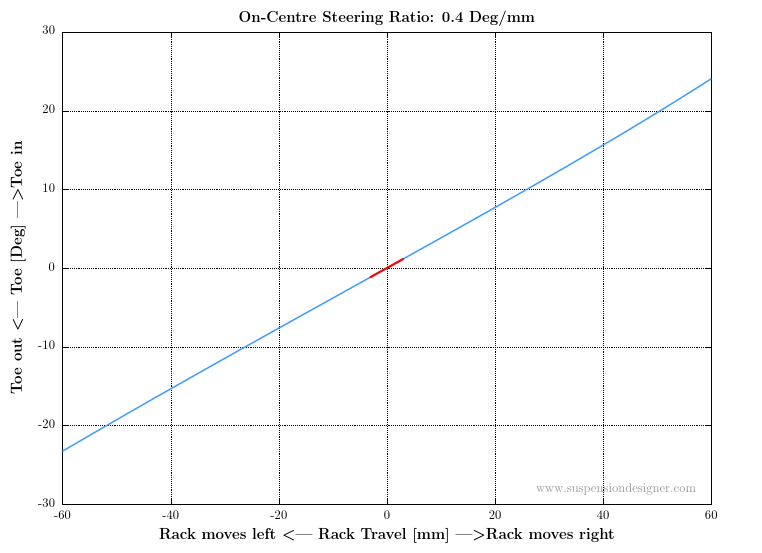
RACE reports the suspension geometry portion of the steering ratio. The metric is given as degrees of toe angle change per mm of rack travel. A typical plot is shown below. In this case the on-centre steering ratio is 0.4 Deg/mm. If the rack ratio is known in mm/rev, the overall steering ratio for the vehicle can be calculated.
—
ENHANCE YOUR CHASSIS AND SUSPENSION SYSTEMS EXPERTISE WITH CUTTING-EDGE SOFTWARE SOLUTIONS AND SUSPENSION COURSES
AUTOMOTIVE/MOTORSPORT SUSPENSION AND CHASSIS SYSTEMS – DESIGN AND ENGINEERING FUNDAMENTALS COURSE
SUSPENSION PERFORMANCE TUNING USING MULTIBODY SIMULATION SOFTWARE COURSE
START USING RACE SOFTWARE TODAY WITH A FREE TRIAL ON ALL PLANS
